SEO is the practice of improving your site’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). But within SEO, there are multiple components, each playing a critical role in driving organic traffic.
One of the most important elements is on-page SEO.
On-page SEO is all about optimising individual web pages to rank higher and generate more relevant traffic.
From keyword optimisation to the structure of your HTML elements, every detail matters when it comes to how search engines interpret and rank your pages.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key aspects of on-page SEO, offering simple yet effective strategies to help improve your search rankings and website performance.
Let’s dive in.
[lwptoc min=”6″ depth=”1″ numeration=”decimalnested” numerationSuffix=”dot” title=”Table of Contents” toggle=”0″ backgroundColor=”#ffffff” borderColor=”#ffffff” linkColor=”#997317″]
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to the optimisation of various elements directly on your website, things like content, URL structure, and internal links.
It differs from off-page SEO, which focuses on actions taken outside your website (think backlinks).
While off-page SEO is important for building your website’s authority, on-page SEO lays the foundation that helps search engines understand what your site is about and how relevant it is to users’ search queries.
But what makes on-page SEO such a key player in your strategy?
It’s simple: On-page search engine optimisation directly impacts your website’s visibility in search results and plays a major role in improving the overall user experience.
By crafting content that aligns with both search engine guidelines and user expectations, you’re helping both sides, making your site easier to find and more appealing to browse.
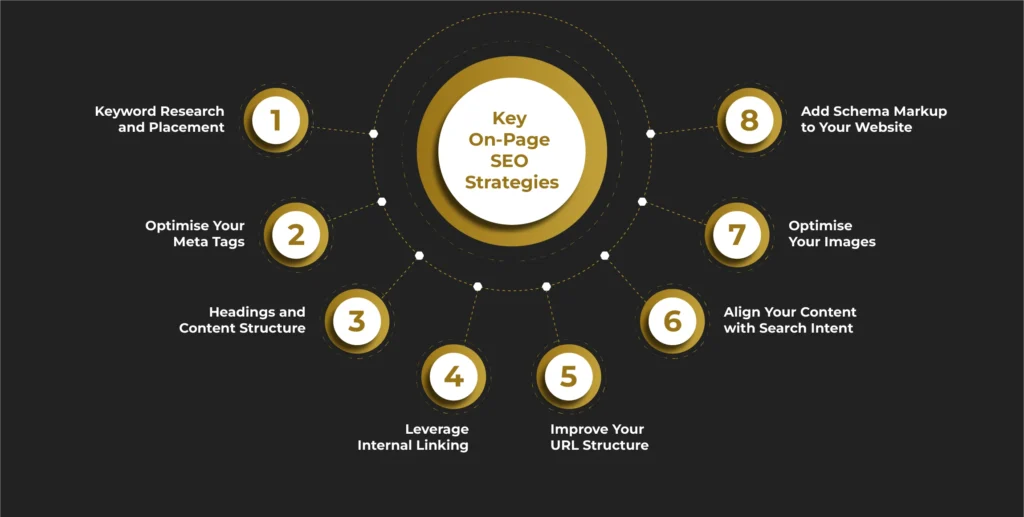
Key On-Page SEO Strategies
When it comes to on-page SEO analysis, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. However, there are some tried-and-tested strategies you can start applying right now to give your website the boost it needs.
1. Keyword Research and Placement
You’ve probably heard it before: Keywords are the backbone of SEO.
But the key isn’t just finding the right keywords, it’s about knowing how and where to place them.
Start with comprehensive keyword research using tools like Google Keyword Planner Semrush, or Ahrefs.
Identify keywords that not only have a decent search volume but also match your content’s intent. (More on this later)
Make a list of your target keywords alongside relevant keyword variations to include in your content, and explore how LSI keywords in 2025: boost your SEO with semantic optimisation can strengthen your strategy further.
Once you’ve got your list of keywords, placement is crucial. Here’s a quick checklist of where they should go:
- Title tag: Include your primary keyword(s) as close to the beginning as possible.
- Headings (H1, H2, etc.): Use relevant keywords in headings, but don’t force them.
- Body content: Naturally integrate your keywords throughout the content, keeping user readability in mind.
- Meta descriptions: Write compelling meta descriptions with your target keywords to improve click-through rates (CTR).
- Alt text for images: Always optimise your images with descriptive alt text that includes relevant keywords.
Pro Tip: Don’t go overboard with keyword placement. Keyword stuffing can land you in all sorts of problems with Google. Your goal should always be to strike a balance between optimisation and readability.
2. Optimise Your Meta Tags
Meta tags are snippets of text that provide important information to search engines about the content on your page. In other words, they help search engines understand the topic, relevance, and structure of the page, influencing how the page is indexed and displayed in search results.
Focus on optimising the following meta tags:
- Title tags: This is the first thing users see in search results. Keep it under 60 characters and make it both keyword-rich and enticing.
- Meta descriptions: Although meta descriptions aren’t a direct ranking factor, they influence click-through rate (CTR). Aim for around 155–160 characters, summarising the content while encouraging users to click.
- Canonical tags: Use these to avoid duplicate content issues by pointing search engines to the preferred version of a page.
- Meta Robots Tag: The meta robots tag tells search engines how to crawl or index your pages. Use this tag strategically to control which pages are indexed and how link equity is distributed across your site.
3. Headings and Content Structure
Headings serve two purposes: they help organise your content for readers and give search engines an idea about the structure and relevance of your content.
Your H1 tag should contain your primary keyword phrase and act as the main title of your page. From there, you can use H2 and H3 tags to break up the content into digestible sections.
To optimise your content for readability, break the text into short paragraphs, use bullet points for lists, and include images to provide a visual break.
A well-organised page keeps users on-site longer, reduces bounce rates, and signals to Google that your page offers value.
4. Leverage Internal Linking
Internal linking is a powerful yet often underutilised on-page SEO technique. By linking to other relevant pages within your site, you’re helping search engines crawl your content and pass authority from one page to another.
Not to mention, it improves the user experience by making it easier for visitors to navigate through your content.
When building internal links, aim for relevant anchor text that describes what the linked page is about. For example:
This not only helps search engines but also gives users an idea of what they’ll find if they click through.
5. Improve Your URL Structure
A clean and concise URL structure is another crucial factor in on-page SEO. Your URLs should be easy to read and should include relevant keywords.
Avoid long, confusing URLs that contain a string of random letters and numbers. Instead, use concise, descriptive URLs that include your primary keywords, providing clarity for both users and search engines.
For example, rather than using an obscure URL structure like www.example.com/2024/138087654, use www.example.com/article-title.
Short, descriptive URLs tend to perform better and are more user-friendly.
6. Align Your Content with Search Intent
One of the most important factors in on-page SEO analysis is ensuring that your content aligns with the search intent of your target audience.
Search intent refers to the underlying goal behind a user’s search query. Understanding this intent can significantly impact your rankings, as search engines aim to provide results that best match what the user is looking for.
There are typically four types of search intent:
- Informational: The user is seeking information (e.g., “what is SEO”).
- Navigational: The user is looking for a specific website or page (e.g., “Facebook login”).
- Transactional: The user intends to make a purchase (e.g., “buy running shoes online”).
- Commercial Investigation: The user is comparing options before making a purchase (e.g., “best SEO tools”).
Tips on aligning your content with the right intent:
- Analyse the search results for your target keywords to see what type of content is ranking.
- Match the format of high-ranking pages (e.g., blog posts, how-to guides, product pages) to deliver content in the most relevant form.
- Make sure your content offers depth and value that matches with what users are searching for, whether that’s educational content, a product purchase, or a comparison.
By aligning your content with search intent, you ensure that it serves both the needs of the user and search engine algorithms. This in turn increases your chances of ranking higher and driving more relevant traffic.
7. Optimise Your Images
Images play a crucial role from both a user experience and SEO perspective. By optimising your images, you don’t just improve your page load speed (an important ranking factor), but also enhance the overall user experience.
Here’s how you can optimise your images for better on-page SEO:
- File Name: Use descriptive, keyword-rich file names for your images. Instead of a generic name like “IMG1234.jpg”, use something like “on-page-seo-strategies.jpg”. This helps search engines understand the content of the image.
- Alt Text: Always include relevant alt text for each image. Alt text is used by search engines to determine the content of the image. Make sure the alt text includes a relevant keyword but remains descriptive and natural.
- File Size: Large image files can slow down your page’s load time, which negatively impacts SEO. Compress images without sacrificing quality to keep load times fast. Tools like TinyPNG or ShortPixel can help with this.
- Image Format: Use modern image formats like WebP where possible, as they offer better compression without sacrificing quality.
8. Add Schema Markup to Your Website
Schema markup is a code that you add to your website to help search engines better understand your content.
By incorporating schema, you can improve how your pages appear in search results, potentially including rich snippets – such as reviews, product details, or event dates – that make your listing stand out and drive more clicks to your page.
Here’s how to effectively implement schema markup:
- Choose the Right Schema Type: Whether it’s a product, recipe, review, or article, make sure you’re using the correct schema type for your content. You can explore different schema types at Schema.org.
- Use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper: Structured Data Markup Helper simplifies the process of generating schema markup, especially for those unfamiliar with coding.
- Test with Google’s Rich Results Tool: After adding schema markup, use the Rich Results Test to confirm that your markup is correctly implemented and that it’s eligible for rich snippets in search results.
Tools and Techniques for On-Page SEO Analysis
While knowing the on-page SEO strategies is half the battle, being able to analyse and measure their effectiveness is equally important.
Luckily, there are plenty of tools to help you perfect an on-page SEO analysis and make necessary adjustments.
1. On-Page SEO Checkers
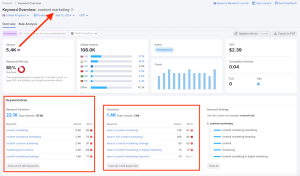
Tools like Google Search Console and Semrush offer comprehensive on-page SEO checkers. These tools analyse your content, meta tags, headings, and more to provide insights into how well-optimised your pages are.
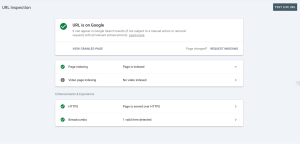
You can use Google Search Console’s Performance Report to see which queries are bringing in traffic and whether your content matches search intent. With the URL Inspection Tool, you can see exactly how Google is crawling and indexing your pages, ensuring there are no major errors.
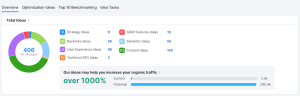
On the other hand, Semrush’s On Page SEO Checker offers detailed analysis for individual pages. The tool runs a thorough audit of your content and meta tags, flagging issues such as missing alt text, keyword gaps, or low content depth.
In addition to identifying problems, Semrush also provides suggestions to improve your pages based on competitive analysis and SEO best practices.
You can track your progress over time and see how implementing these recommendations boosts your rankings.
2. How to Conduct an On-Page SEO Audit
An on-page SEO audit helps you identify areas for improvement. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to conduct one:
- Start with a crawl: Use a tool like Semrush’s Site Audit tool to crawl your website and identify technical issues like broken links, missing meta tags, or duplicate content.
- Review content: Ensure your content is targeting the right keywords and is valuable to your audience.
- Analyse page speed: Fast loading times are a ranking factor, so use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to see where you can optimise images, scripts, and server response times.
- Check mobile-friendliness: Mobile optimization is a must. Use Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability Report to ensure your site is responsive on all devices.
3. Testing and Optimising On-Page Elements
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to test and optimise.
Start by addressing any high-priority issues flagged by your SEO checker.
From there, tweak your meta tags, review your headings, and ensure your content is up to date.
Techniques like A/B testing can help you experiment with different meta descriptions or title tags to see what resonates better with users.
Final Thoughts
Mastering on-page SEO is essential for any business aiming to improve its visibility and attract more organic traffic. By focusing on the key strategies outlined in this guide, such as optimising meta tags, refining content structure, and leveraging on-page SEO tools, you’ll be well on your way to better rankings and a stronger online presence.
However, SEO isn’t a one-time task. It requires regular updates and adjustments to stay competitive as search engines and user behaviour continue to evolve. Learn more about the ever-evolving Google algorithm updates that keep you on your toes and explore The future of SEO: Insights from Niel Patel for expert perspectives.
Don’t just set and forget your on-page SEO, treat it as a crucial part of your long-term digital strategy.
Dominate Your Market with Results-Driven SEO
On-page SEO is just the start. At Dominate Online, we’re committed to delivering more than visibility, we’re focused on results that drive growth. Our comprehensive, data-driven SEO strategies including branded SEO are designed to position your brand as a leader in your industry and help you outpace the competition.
Whether you’re looking for on-page SEO services or need a full-scale digital strategy, we’re here to help you not just compete, but dominate your market.
Let’s turn your digital presence into your strongest business asset – connect with us today, and we’ll guide you to the top of the search rankings.
On-Page SEO FAQs
1. What is the difference between on-page and off-page SEO?
On-page SEO is the process of optimising elements on your website (e.g., content, meta tags), while off-page SEO focuses on external factors (e.g., backlinks and social signals).
2. What are some of the best on-page SEO tools?
We recommend tools such as Google Search Console, Ahrefs, and Semrush for analysing and optimising on-page SEO elements.
3. Are meta descriptions a ranking factor?
No, meta descriptions are not a direct ranking factor. However, they play an important role in influencing click-through rates (CTR) by providing searchers with a summary of what your page is about. A well-written meta description can attract more clicks, which indirectly benefits your SEO performance.
4. How can I make my site mobile-friendly?
To make your site mobile-friendly, focus on using a responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes. This ensures your content looks great on any device. Optimise images to load quickly, streamline your layout for touch navigation, and test your pages with Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability Report to spot any issues.
5. What’s the difference between on-page SEO and technical SEO?
On-page SEO focuses on optimising the content and elements within individual pages (keywords, meta tags, headings, and internal links). It’s all about making sure your content is relevant and easy for both users and search engines to understand.
Technical SEO, on the other hand, deals with the backend aspects of your site (site speed, crawlability, mobile-friendliness, and structured data). It ensures that search engines can properly access, crawl, and index your site for optimal performance in search rankings.